What are the specialized frequency bands used in GNSS?
With the rapid advancement of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology, the design and application of signal frequency bands have become key drivers in improving positioning accuracy, reliability, and security. The evolution of GNSS frequency bands reflects a multi-stage technological progression—from meeting basic navigation requirements to achieving high precision, high stability, and strong anti-interference performance.
At present, all four major global GNSS constellations broadcast multi-frequency signals. Conventional frequency bands such as L1, L2, L5, and L6 together form the foundation of high-precision positioning, supporting a wide range of applications from basic positioning to real-time kinematic (RTK).
Beyond these well-known bands, however, there exist several lesser-known “special frequency bands.” These advanced bands are key to unlocking higher performance and addressing specific application requirements. In this blog, we will take you on a journey to explore the secrets behind these special GNSS frequency bands.
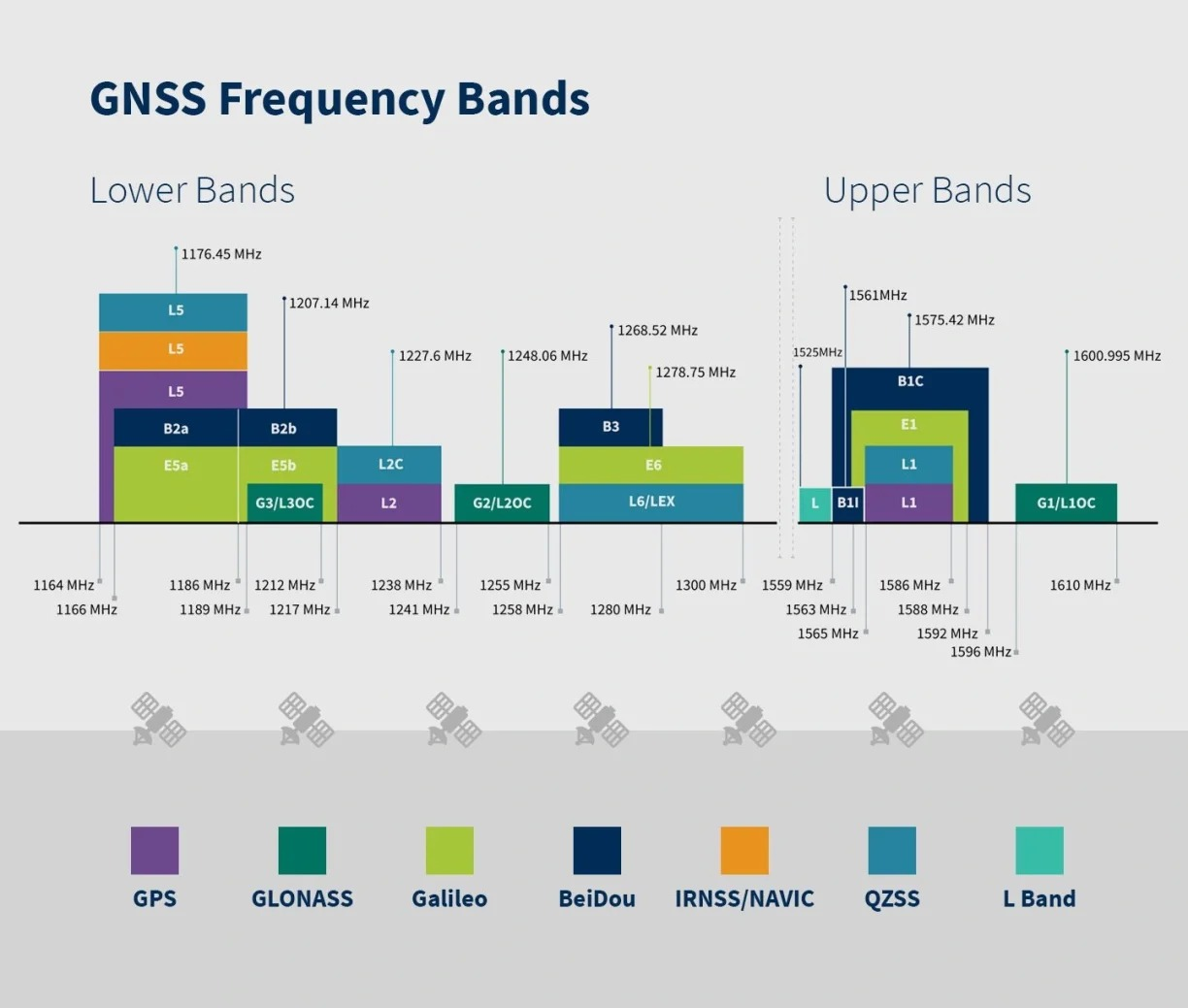
Figure 1. GNSS Frequency Band Diagram(From https://www.taoglas.com/blogs/how-to-leverage-the-l-band-to-balance-accuracy-and-affordability-for-gnss-applications/)
1. L-band
In GNSS applications, L-band mainly refers to the transmission of high-precision positioning correction data via L-band satellite links. Its typical frequency range is 1525 MHz to 1560 MHz.
L-band services broadcast correction information directly to users via satellites. GNSS receivers only need to be equipped with L-band–capable modules to receive these corrections, without requiring any additional network communication. This enables real-time high-precision positioning at the 2–3 cm level.
Thanks to this “direct-to-satellite, network-independent” capability, L-band technology offers significant advantages in regions with weak communication infrastructure or limited terrestrial network coverage, such as oceans, deserts, and high-altitude plateaus.
Both the ComNav K8 and K9 series models support L-band frequency reception at the hardware level.
2. S-band
In radio spectrum allocation, the S-band covers the frequency range of 2–4 GHz. This band offers relatively wide bandwidth and favorable signal propagation characteristics, and has long been widely used in telemetry, tracking and control (TT&C) as well as radar systems.
In satellite navigation systems, the S-band navigation frequency is 2498.028 MHz. Currently, India’s NavIC system uses this frequency in combination with the L5 band (1176.45 MHz). This dual-frequency configuration enables more effective correction of ionospheric errors, thereby achieving more stable and reliable high-precision positioning compared to single-frequency solutions.
At present, ComNav Technology has already mastered the reception and processing of S-band signals.
3. SBAS-PAK /SBAS-SouthPan
3.1 SBAS-PAK
Pakistan has developed Pakistan Space Based Augmentation System (Pak-SBAS) for improving the accuracy, integrity and reliability of existing Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) service. Pak-SBAS will enable meter to sub-meter positioning which will fulfill the precise positioning requirements of civil/public users cis & trans frontier.
The SBAS-PAK service coverage extends across Pakistan and surrounding regions of South Asia. The system broadcasts SBAS augmentation signals on the L1 (1575.42 MHz) and L5 (1176.45 MHz) bands, providing orbit and clock corrections, ionospheric delay corrections, and system integrity monitoring. The target positioning accuracy is 1–2 meters. The system is currently under construction and in the trial operation phase (2024–2025).
Once completed, SBAS-PAK will significantly enhance civil aviation navigation safety and positioning accuracy in South Asia, while also delivering meter-level real-time positioning capabilities for civilian applications such as UAV surveying, mapping, and geospatial information services.
ComNav has already enabled support for SBAS-PAK services across its K9 series modules and terminal products.
3.2 SBAS-SouthPan
SouthPAN (Southern Positioning Augmentation Network) is the first satellite-based augmentation system in the Southern Hemisphere, jointly developed by Australia and New Zealand, designed to provide navigation augmentation services comparable to WAAS and EGNOS in the region.
SouthPAN is a “next-generation SBAS”, which means that-in addition to delivering an Open Service augmenting the GPS L1-C/A navigation signal-we also transmit a Dual-Frequency Multi-Constellation (DFMC) Open Service augmenting the GPS L1-C/A and L5 navigation signals, and Galileo E1 and E5a navigation signals. The aviation sector globally are working towards standardising DFMC services as the primary future SBAS, providing improved integrity and precision.
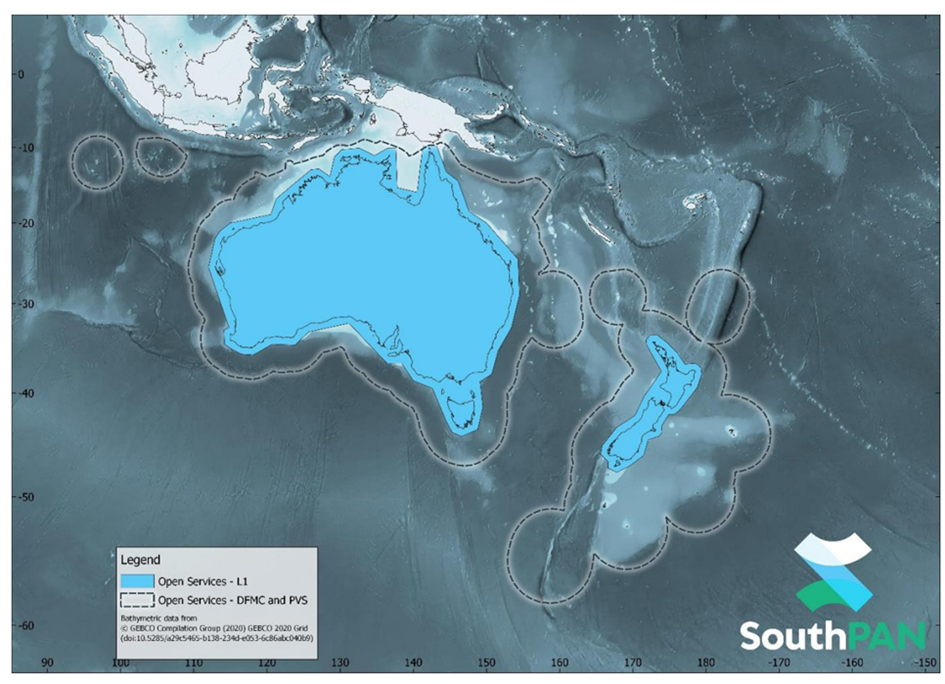
Figure 2. SouthPAN early Open Services coverage. OS-L1 covers mainland Australia and New Zealand. OS-DFMC and OS-PVS cover both countries Exclusive Economic Zones
Since 2022, SouthPAN has entered the testing and operational phase. Once fully deployed, the system will provide stable, continuous, and high-precision satellite positioning for Australia, New Zealand, and surrounding regions, supporting a wide range of applications in civil aviation, agriculture, automation, and geospatial industries.
ComNav’s K8 and K9 series modules and terminal products already support SBAS-SouthPAN services.
4. PPP-B2B and PPP-HAS
4.1 PPP-B2B
PPP-B2b (Precise Point Positioning via B2b signal) is a real-time high-precision positioning service provided by China’s BeiDou-3 system. It broadcasts precise corrections via B2b frequency (1207.14 MHz) from BeiDou GEO satellites. The signal uses QPSK modulation with a 24 MHz bandwidth, containing precise orbit and clock corrections, ionospheric delay corrections, and satellite health information. All correction data are generated in real time by the national satellite navigation ground monitoring system and updated at approximately 1 Hz.
The PPP-B2b service covers the Asia-Pacific region, enabling users to achieve centimeter-level positioning without requiring a network connection. Under ideal conditions, the system can achieve horizontal accuracy within 10 cm and vertical accuracy within 20 cm, with a typical convergence time of 10–30 minutes. As the world’s first officially operational satellite-based PPP broadcast service, PPP-B2b makes high-precision positioning truly “offline-capable”, making it particularly suitable for scenarios with low network dependence, such as marine surveying, autonomous agricultural machinery, UAV mapping, and field operations.
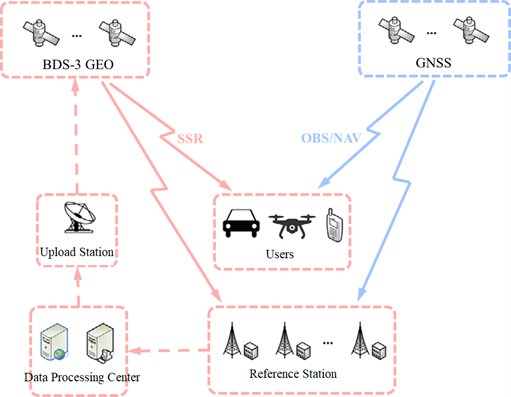
Figure 3 PPP-B2b service system
ComNav Technology leads to carry out PPP-B2b signal-related research and applies PPP-B2b technology and real-time Precision Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm to high-precision products, achieving real-time high-precision positioning without relying on communication networks. More details please refer to this blog: https://www.comnavtech.com/about/blogs/379.html
ComNav’s K8 and K9 series modules and terminal products already support PPP-B2b services.
4.2 PPP-HAS
PPP-HAS (High Accuracy Service) is a global satellite-based PPP broadcast service provided by Europe’s Galileo system. It transmits precise correction data to users worldwide via the E6-B frequency (1278.75 MHz). The signal uses BPSK(5) modulation and is directly downlinked from MEO satellites, providing global coverage.
The broadcast data of PPP-HAS include precise orbit and clock corrections, signal biases (code and phase biases), and satellite health information, using the RTCM-SSR data format, consistent with PPP-B2b, which ensures good cross-system compatibility.
Galileo HAS has now entered its official service phase (Phase 1) and is freely accessible to users worldwide. Once converged, the positioning performance can reach horizontal accuracy within 20 cm and vertical accuracy within 40 cm, with a typical convergence time of 5–20 minutes. Unlike BeiDou’s regional PPP-B2b service, PPP-HAS achieves global coverage through multiple MEO satellites, offering stronger continuity and availability. It is well-suited for applications such as precision agriculture, aviation navigation, and high-precision geospatial services worldwide.
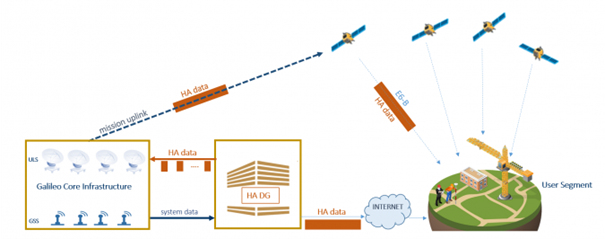
Figure 4 PPP-HAS service system
ComNav’s K8 and K9 series modules and terminal products already support PPP-HAS services and have undergone testing and verification. For detailed information, please refer to the blog:https://www.comnavtech.com/about/blogs/474.html
5. CLAS
CLAS (Centimeter-Level Augmentation Service) is a high-precision satellite positioning service provided by Japan’s QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System). It is the world’s first real-time centimeter-level positioning system openly available to general consumer terminals.
The service broadcasts PPP correction data—including precise ephemerides, satellite clock corrections, and ionospheric grid corrections—via the QZSS L6D frequency (1278.75 MHz), allowing users to achieve high-precision positioning without any terrestrial network connection.
CLAS delivers real-time PPP positioning accuracy of 2–5 cm horizontally and within 10 cm vertically, with a convergence time of approximately 30–60 seconds. Its coverage spans Japan and surrounding areas up to roughly 1,500 km, making it particularly suitable for applications such as autonomous driving, precision agriculture, UAV surveying, and geospatial data collection.
The launch of CLAS marks the transition of satellite PPP technology from research to commercial applications, laying the foundation for future widespread high-precision positioning.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.