How does Dual-board Heading Work?
1 What is dual-board heading?
Dual-board heading uses two GNSS boards to achieve high-precision heading. By receiving positional information from two antennas, the internal algorithms and data processing of the boards calculate the device's attitude and azimuth. Dual-board heading has wide applications in high-precision positioning, navigation, autonomous driving, and surveying. So, how can we perform dual-board heading using two SinoGNSS K803 boards?
2 Principle of dual-board heading
Dual-board heading relies on two independent GNSS boards that receive satellite signals from two antennas. The main principles include the following:
(1) Baseline vector calculation
The fixed distance between the two antennas is referred to as the baseline. By receiving satellite signals at the same time, the two boards can calculate the relative displacement and direction between the antennas, and this vector is the baseline vector.
(2) Phase difference calculation
When two antennas receive signals from the same satellite, a phase difference occurs due to their different positions. By accurately measuring this phase difference, the GNSS board can calculate the relative angle between the antennas to get the heading of the device.
(3) Heading and pitch calculation
The direction of the baseline vector aligned with the earth coordinate system helps the boards calculate the device's heading. With the combination of the baseline length and the signals received by the two antennas, the system can accurately output the device's heading and pitch.
3 Dual-board heading configuration
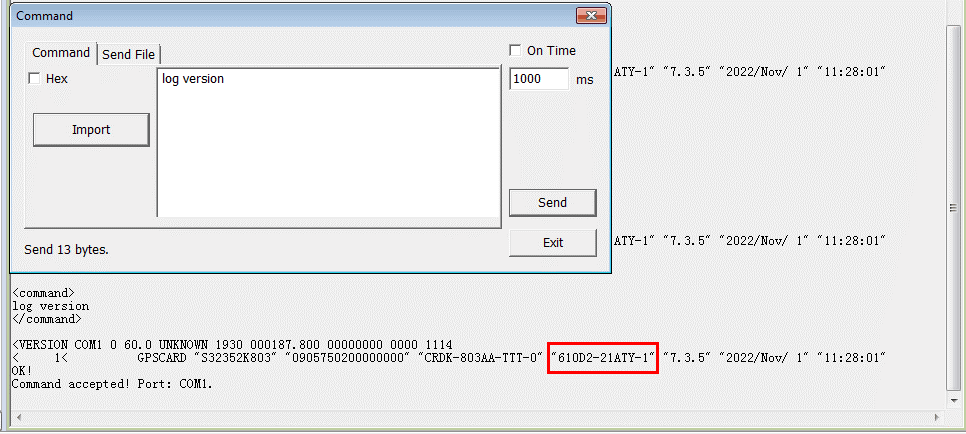
(1) Firmware upgrade
Upgrade the firmware of two SinoGNSS K803 to 610D2.
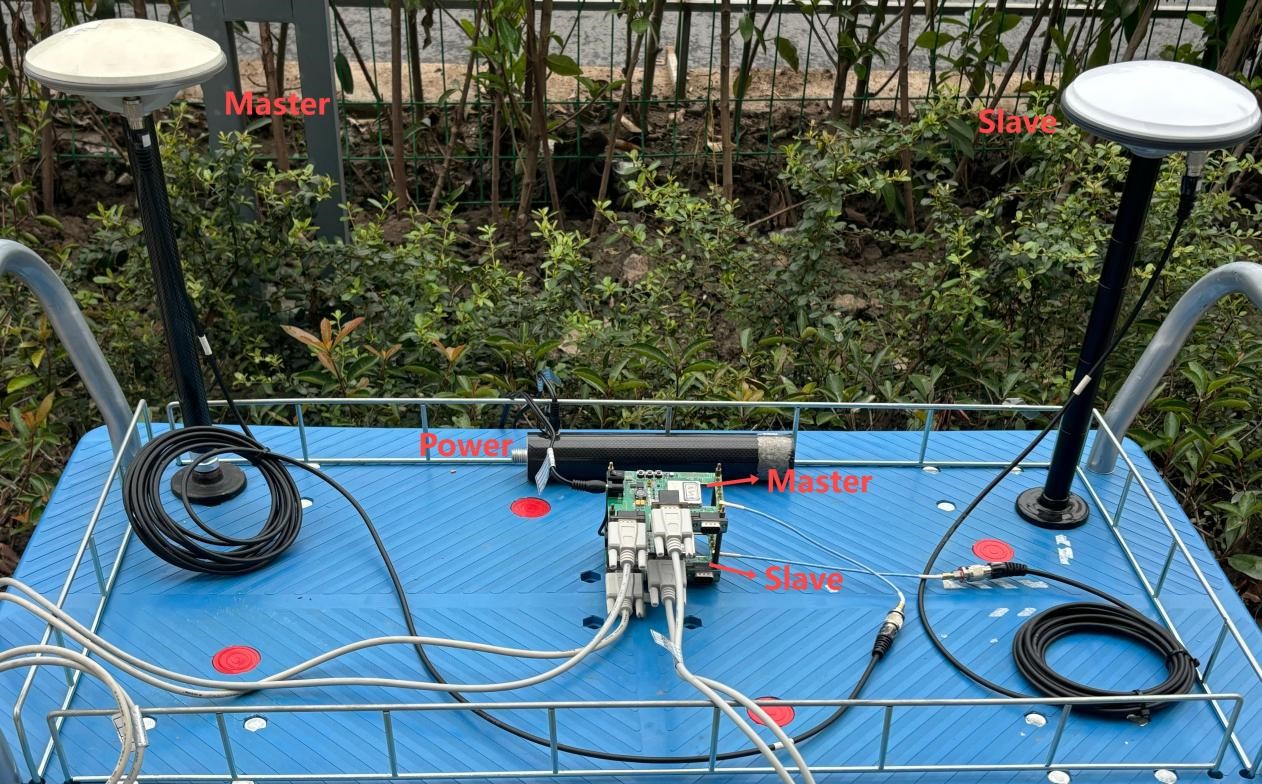
(2) Hardware setup
Antenna layout: Two antennas need to be installed at a certain baseline distance. Usually the longer the baseline length, the higher the directional accuracy. The antennas should be installed parallel to each other to avoid tilting.
Board connection: Connect the two K803 boards to the two antennas respectively, ensuring a stable connection between the antennas and the board interfaces. Keep the antennas away from obstructions to guarantee optimal satellite signal reception. Connecting com4 of the master to com4 of the slave.
(3) Software setup
Differential signal configuration: Dual-board heading requires differential data support, with the two boards exchanging differential data via protocols such as RTCM. Ensure that the differential signal transmission for the boards is properly configured.
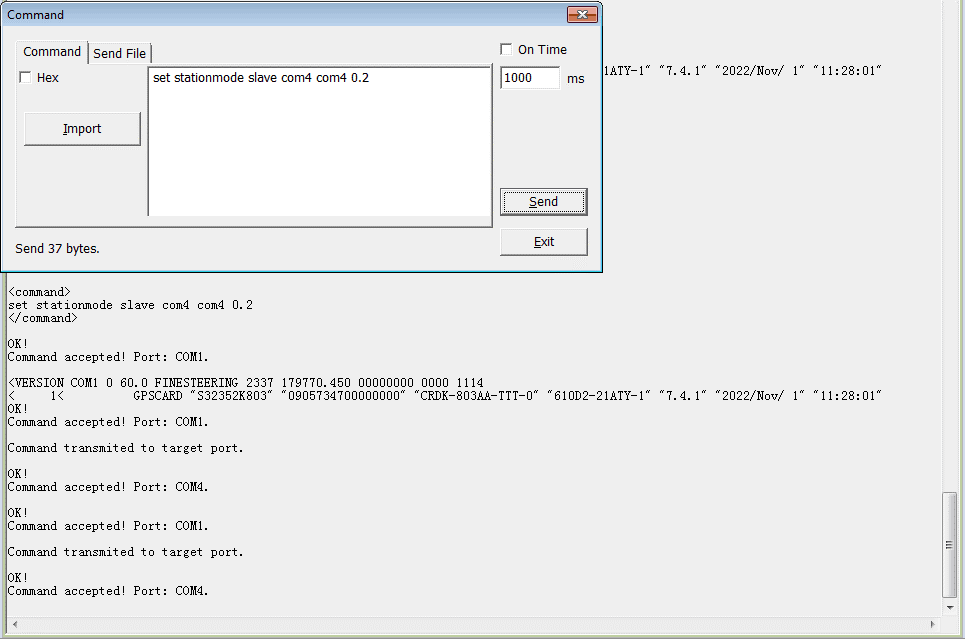
➥ Master configuration
Set com4 transit differential data and set com4 receive differential data from slave. Differential data transmission interval is 0.2s. Set the baudrate to 921600 and save the current configuration. The commands are as follows:
set stationmode master com4 com4 0.2
com com4 921600
saveconfig
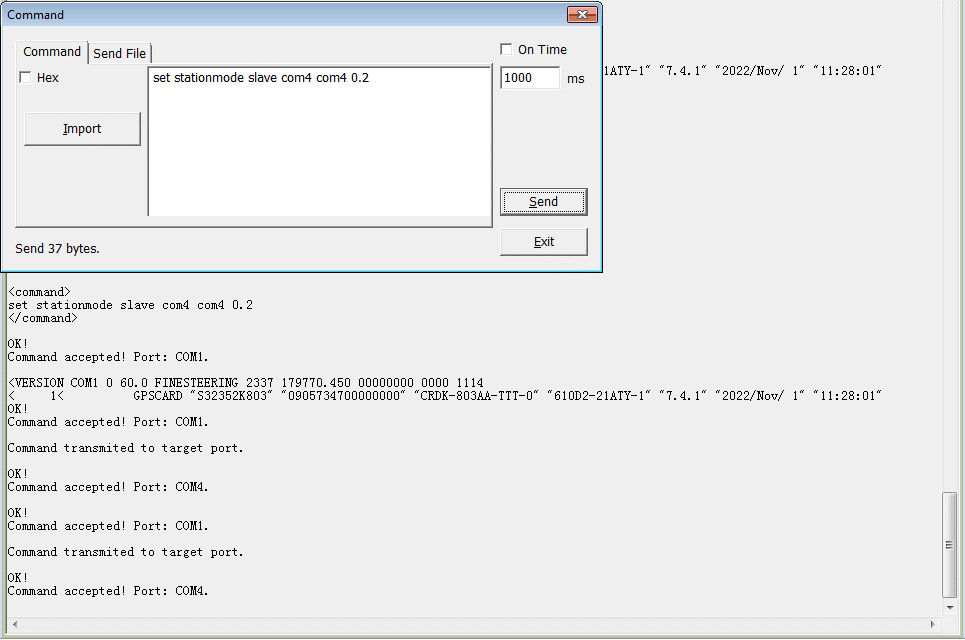
➥ Slave configuration
Set com4 receive differential data from master and set com4 transmit differential data. Differential data transmission interval is 0.2s. Set the baudrate to 921600 and save the current configuration. The commands are as follows:
set stationmode slave com4 com4 0.2
com com4 921600
saveconfig
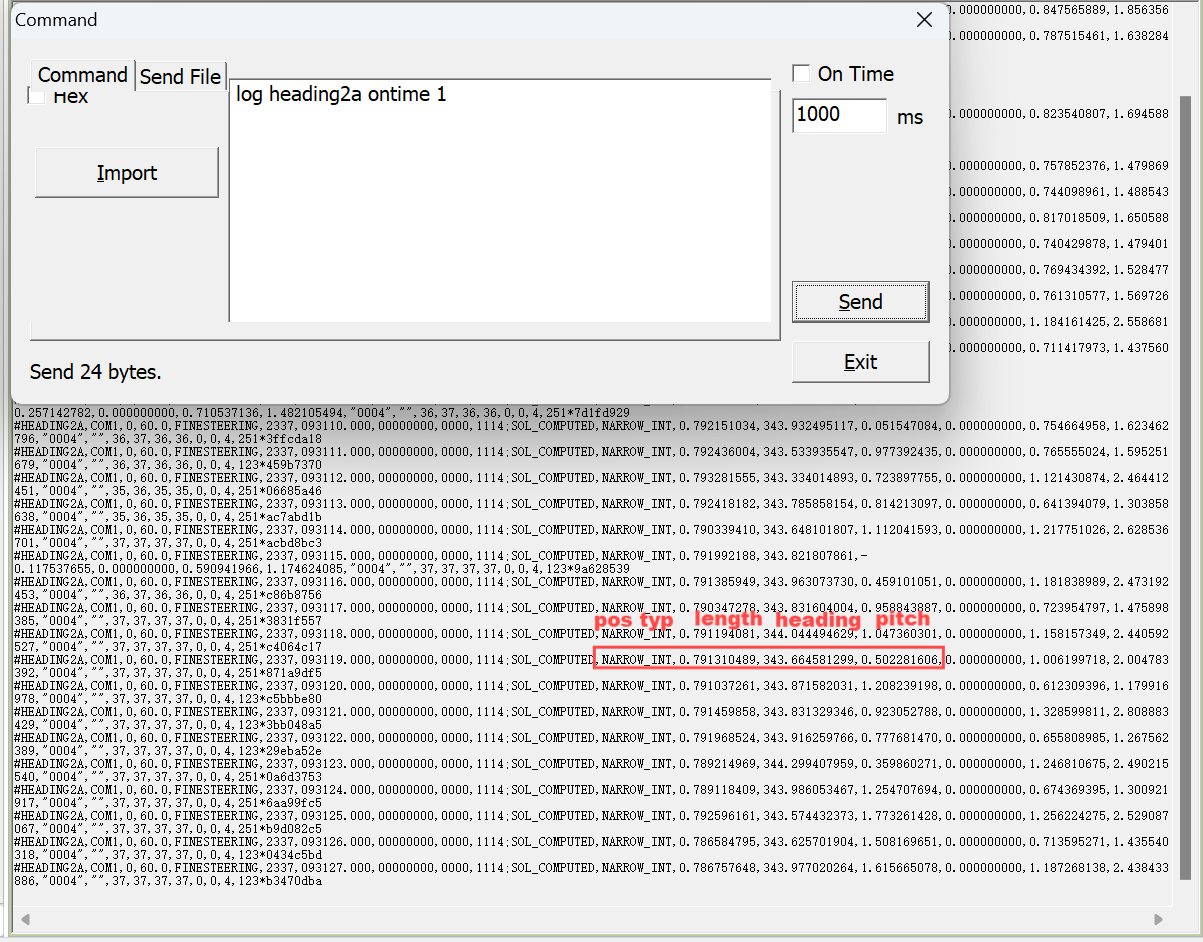
Heading information output: The heading2a is the heading information between the master and the slave. The heading information such as positioning type, baseline length, heading and pitch can be obtained by log heading2a ontime 1.
log heading2a ontime 1
Note: NARROW_INT is the positioning type, denoting the fixed solution.
4 Conclusion
Dual-board heading technology provides a reliable solution for applications requiring high-precision directional control. For instance, in autonomous vehicles, it accurately determines the driving direction and integrates with navigation systems to ensure precise driving. In marine surveying with unmanned vessels, it assists in positioning and maintaining heading. Through precise baseline vector calculations and phase difference resolutions, the device can quickly obtain heading and pitch information. With the advancement of GNSS technology, the application range and accuracy of dual-board heading will further improve in the future, delivering more efficient positioning solutions for various industries.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.






