The Magic Behind RTK: Delivering Unparalleled Positioning Precision

1 Understanding RTK (Real-Time Kinematic)
RTK, or Real-Time Kinematic, is a satellite navigation technique fundamentally crafted to enhance the precision of position data procured from satellite-based positioning systems like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou.
Imagine you're on a vast open field, trying to determine your position using a conventional GPS. Typically, you might get accuracy within a few meters. Now, introduce RTK into the scene, and suddenly, you're pinpointing your location with an incredible centimeter-level accuracy! This leap in precision is achieved by RTK's unique ability to correct GPS signals, thereby setting itself leagues apart from other positioning methods.
2 RTK vs. PPK: What's the Difference?
While diving into the world of high-precision satellite navigation, you're bound to come across PPK or Post-Processed Kinematic. On the surface, RTK and PPK might seem like twin siblings, but they have distinct operational differences.
The most significant distinction lies in the timing of data correction:
So, when deciding between RTK and PPK, it boils down to whether you need immediate precision as you go (RTK) or if you're okay with collecting data first and achieving precision later (PPK).
To achieve the most from RTK technology, correct configuration is imperative. The test was done using a K8 series module.Here are the recommended configuration steps based on RTCM3.0/3.2, the standardized message format for differential correction:
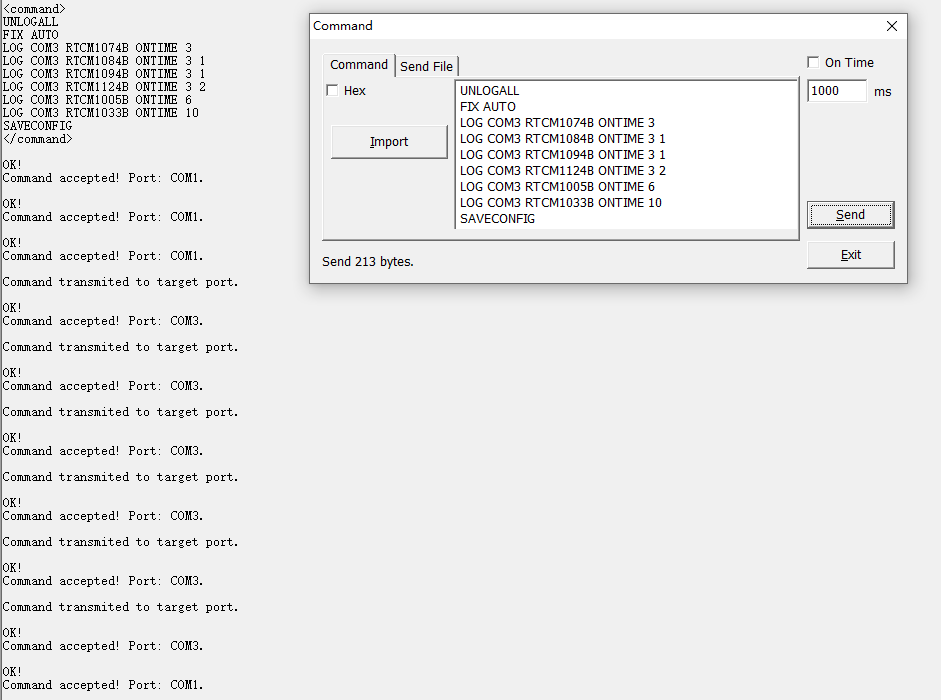
Radio Base station--RTCM3.2 MSM4
Here shows commands of RTCM with different format, including RTCM3.0, RTCM3.2 MSM4, RTCM3.2 MSM5.
If use radio modem for data link communication between Base and Rover, as considering limited data size can be sent per second, there suggest use subcontracting strategy for base transmit different constellations.
| RTCM3.0 | For the Base |
|---|---|
| Unlogall | // Clear previous settings |
| Fix position 31.1744880 121.3878091 44.1287 | // Fix the coordinate B, L, H |
| (Fix auto) | // Fix auto |
| Log comX rtcm1004b ontime 1 | // Extended L1, L2 GPS RTK Observables |
| Log comX rtcm1012b ontime 1 | // Extended L1, L2 GLONASS RTK Observables |
| Log comX rtcm1005b ontime 5 | // Base station coordinate |
| Log comX rtcm1033b ontime 10 | // Base station type |
| Saveconfig | // Save configuration |
| RTCM3.2 (MSM4) | For the Base |
|---|---|
| Unlogall | // Clear previous settings |
| Fix position 31.1744880 121.3878091 44.1287 | // Fix the entered coordinate |
| (Fix auto) | // Fix the coordinate automatically |
| Log comX rtcm1074b ontime 1 | // GPS Full PRs and Phase Ranges plus CNR |
| Log comX rtcm1084b ontime 1 | // GLONASS Full PRs and Phase Ranges plus CNR |
| Log comX rtcm1094b ontime 1 | // GALILEO Full PRs and Phase Ranges plus CNR |
| Log comX rtcm1124b ontime 1 | // BeiDou Full PRs and Phase Ranges plus CNR |
| Log comX rtcm1005b ontime 5 | // Base station coordinate |
| Log comX rtcm1033b ontime 10 | // Base station type |
| Saveconfig | // Save configuration |
| RTCM3.2 (MSM4)(radio) | For the Base |
|---|---|
| Unlogall | Same as above |
| Fix position 31.1744880 121.3878091 44.1287 | |
| (Fix auto) | |
| Log comX rtcm1074b ontime 3 | |
| Log comX rtcm1084b ontime 3 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1094b ontime 3 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1124b ontime 3 2 | |
| Log comX rtcm1005b ontime 6 | |
| Log comX rtcm1033b ontime 10 | |
| Saveconfig |
| RTCM3.2 (MSM5) | For the Base |
|---|---|
| Unlogall | Same as above |
| Fix position 31.1744880 121.3878091 44.1287 | |
| (Fix auto) | |
| Log comX rtcm1075b ontime 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1085b ontime 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1095b ontime 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1125b ontime 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1005b ontime 5 | |
| Log comX rtcm1033b ontime 10 | |
| Saveconfig |
| RTCM3.2 (MSM5)(radio) | For the Base |
|---|---|
| Unlogall | Same as above |
| Fix position 31.1744880 121.3878091 44.1287 | |
| (Fix auto) | |
| Log comX rtcm1074b ontime 3 | |
| Log comX rtcm1084b ontime 3 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1094b ontime 3 1 | |
| Log comX rtcm1124b ontime 3 2 | |
| Log comX rtcm1005b ontime 6 | |
| Log comX rtcm1033b ontime 10 | |
| Saveconfig |
| For the Rover | |
|---|---|
| log comX gpgga ontime 1 | // ComX output GPGGA data |
| Interfacemode comX auto auto on | // Config comX to detect RTCM corrections |
| Saveconfig | // Save configuration |
Tip: If comX is the serial port used for configuration currently, please replace command saveconfig with interfacemode saveconfig.
Upon successful configuration, you can check the OEM board's mode with the `$GPGGA` message. If it's in RTK mode, the solution status should display as “E,4”. $GPGGA,015101.00,3121.0000551,N,12117.5483125,E,4,23,1.1,37.2598,M,0.000,M, 02,0004*58
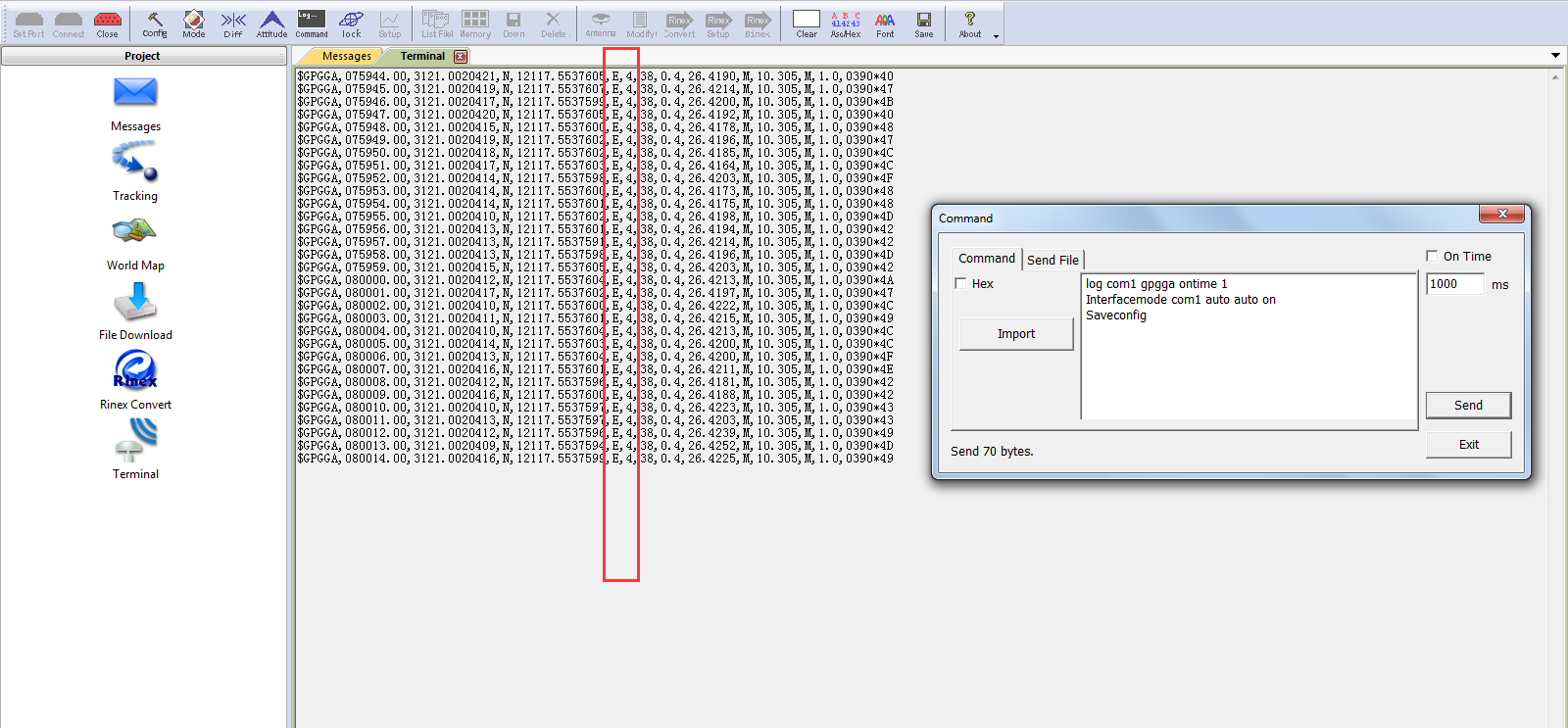
Rover-RTK fixed
Moreover, the default setting is survey mode, and you will need adjust to correct dynamic mode according to your applications. For example the device used for land survey, you can use default mode “survey”, if the device used on robot, you will need set the mode to “robot”. In different mode, RTK engine treats the observation data in different style to promote the performance of RTK engine. The command is as below:
| SET APPSCENE <mode> | survey/robot/car/air/space |
| Saveconfig | Save configuration |
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.