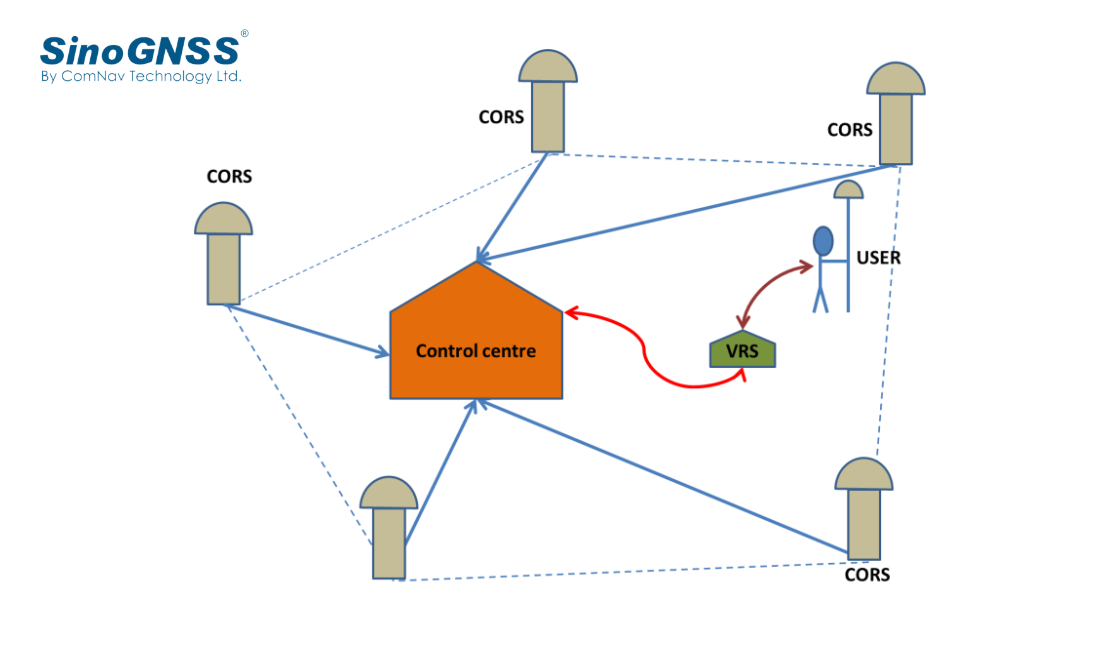
VRS Principle & Performance of CDC.NET+CORS
1 Brief Introduction of the Principles of CORS, Network RTK and VRS
CORS, also known as Continuously Operating Reference Stations, is one or several fixed and continuously operating GNSS reference stations, with the combination of computers, data communications and Internet (LAN/WAN) technologies to automatically provide multiple needs of users with different kinds of GNSS observations (carrier phase, pseudorange), various corrections, status and other GNSS service systems in real time.
GNSS network RTK, also known as multi-reference station RTK, is a positioning method that establish multiple (generally three or more) GNSS reference stations in an area to form a mesh coverage, and calculate and broadcast the GNSS correction information based on one or more of these reference stations and make real-time corrections to GNSS users in this area.
Virtual Reference Station. refers to certain number (at least three) of reference stations are set up in an area to receive satellite signals and transmit the information to the information processing center. The rover sends the location information of the receiver to the data processing center, and the data processing center will select the information of several nearby reference stations to "virtually" create a reference station based on the location of the mobile station, then broadcast the corrected data of the virtual reference station to the mobile station. The position of this virtual reference station is usually within 5 kilometers around the mobile station, but in fact, it is usually within a few meters. The error of the data obtained through this technology is greatly reduced.
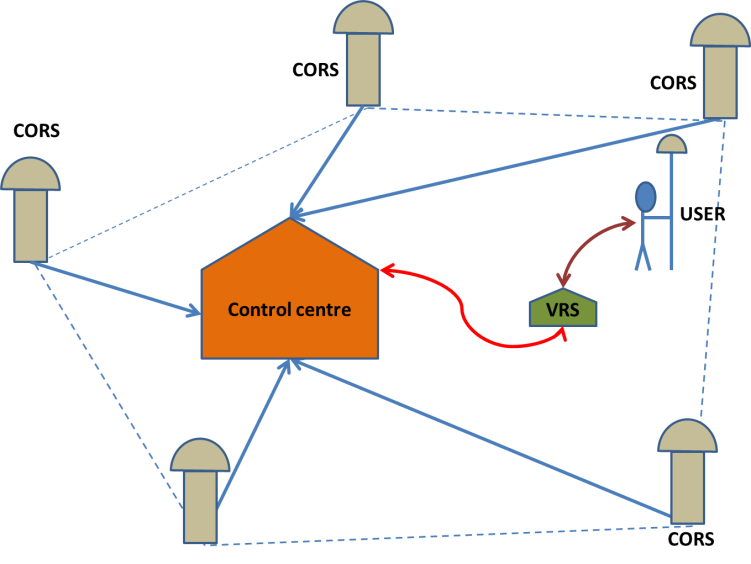
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of VRS working principle
2 Comparison and Analysis of Several Network RTK Technologies
VRS | FKP | MAC | CBI | |
Basic mathematical model | Interpolation model of double-difference observation model | Kalman Filtering of Non-Difference Observation Model of the Whole Network Global Solution | Double-difference observation model / compatible model | Interpolation model of double-difference observation model |
Spatial error model | On the server side | On the mobile user side | On the mobile user side | On the server side |
Reference station participating in the calculation | Need to select a master reference station, and all reference stations in the network participate in the positioning calculation | Do not select the main reference station, take the three closest reference stations to the rover | Need to select a master station, but it is not required to use the base station closest to the user as the master station | Flexible selection of the reference station according to the relative position of the rover and the reference station |
Communication mode | Two-way communication | One-way communication | Two-way and one-way communication | One-way communication |
GPSNet of Trimble | SAPOS network of Germany | Spider of Leica | PowerNet of Wuhan University |
3 VRS Fundamental
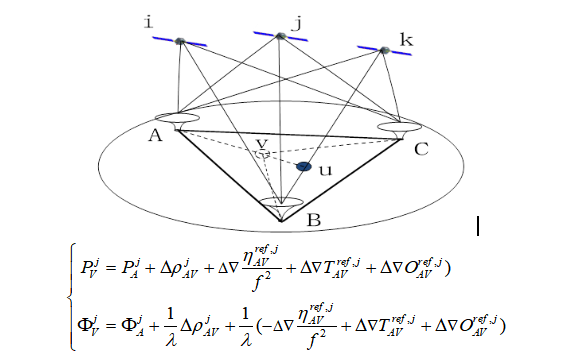
The first is the fixation of the long baseline ambiguity of the base station. How to achieve fast and accurate fixation of the long baseline ambiguity is a key factor that affects the initialization time and availability of the system.
The second is the accurate modeling of regional spatial atmospheric errors. The modeling accuracy of atmospheric errors directly affects the positioning accuracy of users.
Real-time transmission, encoding and decoding of data in different formats
Data quality control, processing of related errors such as cycle slip, clock slip, and multipath;
Concurrent processing when large-capacity users access;
1) Fixing the ambiguity of the baseline
a) Wide lane ambiguity
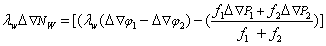
b) Deionospheric combination
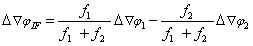
c) L1 ambiguity and zenith tropospheric delay RZTD (tropospheric effect is negligible for short baselines and does not need to be estimated, but needs to be estimated for long baselines)
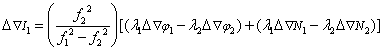
2) Calculation of baseline atmospheric error delay
a) Calculation of double-difference ionospheric delay
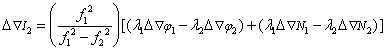
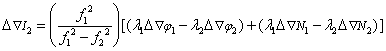
b) Calculation of double-difference tropospheric delay
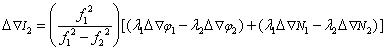
3) Linear interpolation of tropospheric and ionospheric delays at virtual reference stations
4) Comprehensive Correction Number Generation of Virtual Reference Station
a) Comprehensive correction parameters:
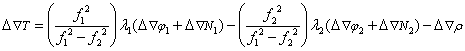
b) Non-difference observations:
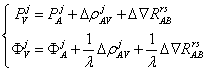
4 Performance of CDC.NET + M300pro
The CDC.NET software is deployed on a physical server, with the environment configured to:
Item | Server configuration |
Unit type | 10SMCTO1WW |
Equipment characteristic | Intel(R)Core(TM)i5-8500CPU@3.00GHz,8GMemory installed |
OS | Windows10 64bit(10.0, version17763) |
Data base | MySQL5.5 |
Software version | CDC.NET 1.8.2 |
The test results:
Item | Performance |
System initialization time | Less than 2 minutes |
Rover initialization time | Less than 30 seconds |
Precision of inner coincidence | Horizontal 1.4cm and vertical 2.3cm |
Precision of outside coincidence | Horizontal 1.9cm and vertical 2.6cm |
Number of Base station access points | The reference station access number is 220, and the program is still stable |
Concurrent online users | Grid mode can reach a maximum capacity of more than 10,000 users |
System stability | The 100 Bases and 500 Rovers can operate stably for more than 30 days |
Two K708 boards(both firmware are 399A5) connected to the same antenna are connected to VRS services for CDC.NET 1.8.2 and NEAREST services for CDC +, respectively,to compare the positioning accuracy. The base station selected for connecting CDC + single base station service is MLHU (8KM from the rover),the station network connected to the VRS service is shown in below figure, the net-element is KUNS-JHZX-MLHU, the main reference station is MLHU, and the distance from the main reference station to the rover is 8KM.
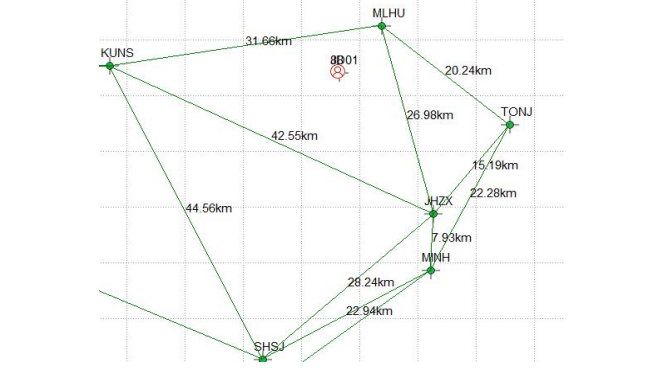
VRS and SRTK positioning comparison
Positioning mode | Horizontal RMS(m) | Vertical RMS(m) | Horizontal range (m) | Error overrun rate | Fixed rate |
VRS | 0.0073269 | 0.01224 | 0.04 | 0.86% | 100% |
NEAREST | 0.0061154 | 0.01021 | 0.03 | 0.45% | 100% |
The number of satellites calculated by the two modes is the same, the Horizontal and vertical positioning accuracy of VRS is slightly lower than that of SRTK, The error overrun rate was also higher than that in the SRTK, further optimization is still needed.
Through actual testing and verification, CDC.NET's network RTK positioning accuracy is within the range of 80km on a side, and can reach the positioning accuracy of 2cm horizontally and 3cm vertically in the network, which is better than the horizontal 10cm+D×10-6 and vertical 10cm+D×10-6 positioning accuracy required by the system design. And the system positioning continuity, usability, initialization fixed time and other indicators all meet the RTK positioning performance indicators, which is at the leading level in the industry.
Notes:
1. Some pictures of the article are taken from the Internet, if you have any questions, please contact us in time.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.