How to analyze GNSS signal quality
With the rapid development of high precision GNSS technology, more and more industries have adopted the GNSS technology for positioning and navigation, such as traditional applications like surveying & mapping, machine guidance, GIS, and the new trends like automated driving, IoT and smart city. No matter for what kind of applications, the positioning accuracy and reliability is of great importance. It depends on the positioning algorithm on one hand, and the GNSS signal quality on the other.
From the users’ point of view, it is difficult to judge the algorithm when evaluating a GNSS device. As for the signal quality, there are several indicators to evaluate such as integrity, multi-path and SNR. This blog will introduce how to analyze the GNSS signal quality based on SNR indicator.
SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) is indicating the relationship between carrier signal and carrier noise, which equals to carrier power/noise power. In the satellite communication system, the best antenna arrangement can get the best SNR. A high SNR can provide a better network reception rate, better network communication quality, and better network reliability. It is one of the important indicators for evaluating carrier phase observations.
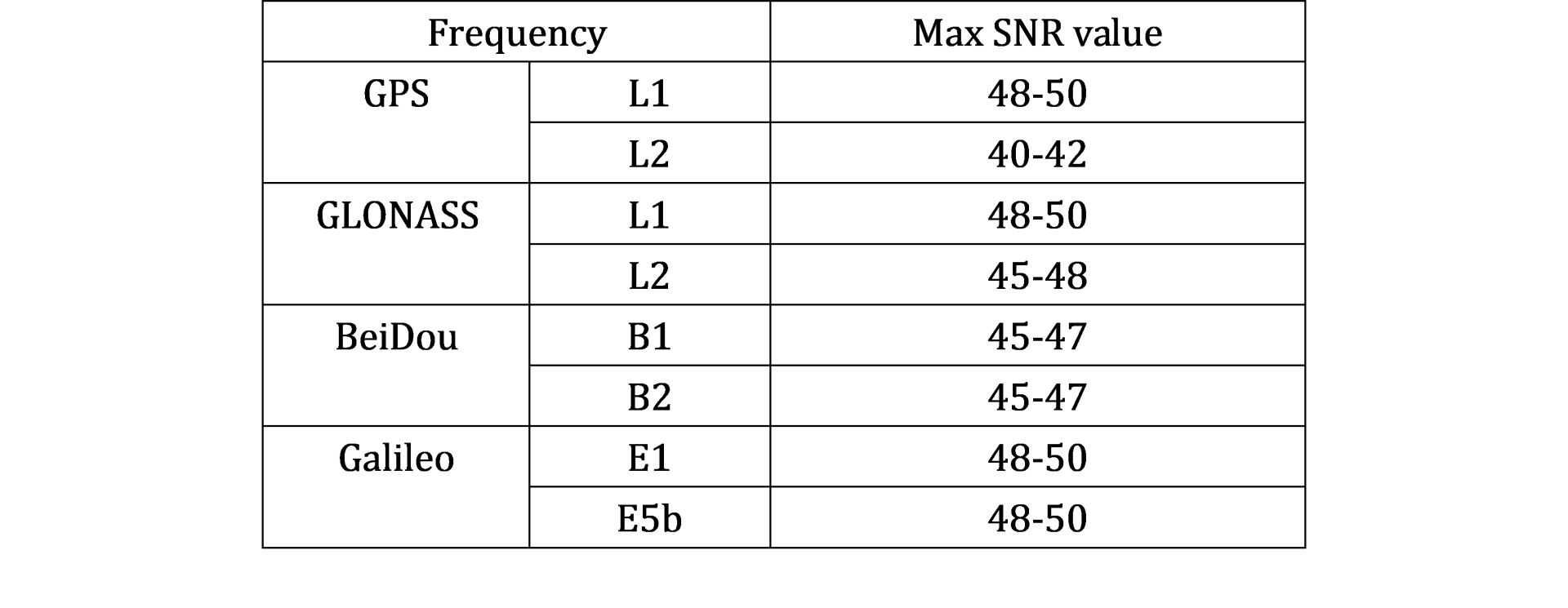
However, the standard value of SNR for each constellation and each frequency is not the same. Users need to evaluate to signal quality one by one satellite referring to the theoretical value. So sometimes it is not convenient for users to get a quantitative solution to evaluate the signal quality.
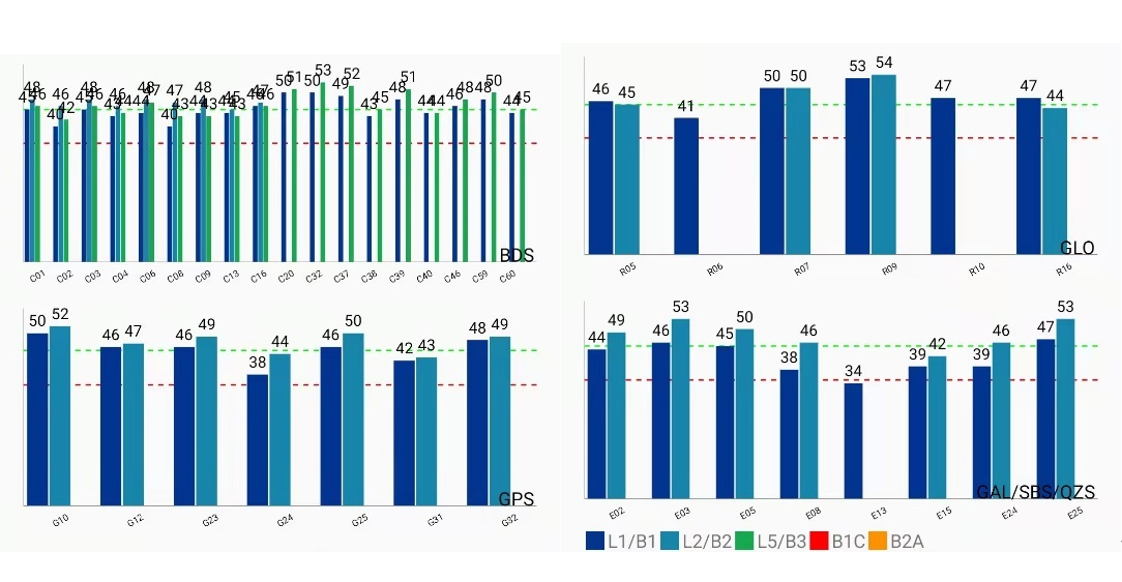
In order to simplify the analyze process and let users evaluate the signal quality more intuitively, the R&D team of ComNav Technology defined a SNR score for an overall evaluation. This indicator can measure the ability of a GNSS receiver to receive signals and reflect its signal tracking and acquisition performance. Its short-term oscillation can reflect the signal interference by other factors. When researching and analyzing the SNR, the R&D team of ComNav Technology mainly extracted the SNR in the GNSS observation data, and uses the method of averaging to calculate its index value.
1. Theoretical SNR – Calculated the theoretical value of each satellite on each frequency at each epoch based on the elevation cutoff angle.
2. Actual SNR – Extracted the actual SNR value of each satellite on each frequency at each epoch from the GNSS raw data.
3. SNR score - The SNR score of each satellite on each frequency at each epoch is equal to the actual SNR value/theoretical SNR value × 100%
4. SNR score of each epoch – The average value of SNR scores for every satellite and every frequency at the same epoch.
Data quality evaluation standard:
The higher the SNR score, the closer the actual SNR is to the theoretical SNR, indicating that the signal is less interfered by other factors and the data quality is more reliable.
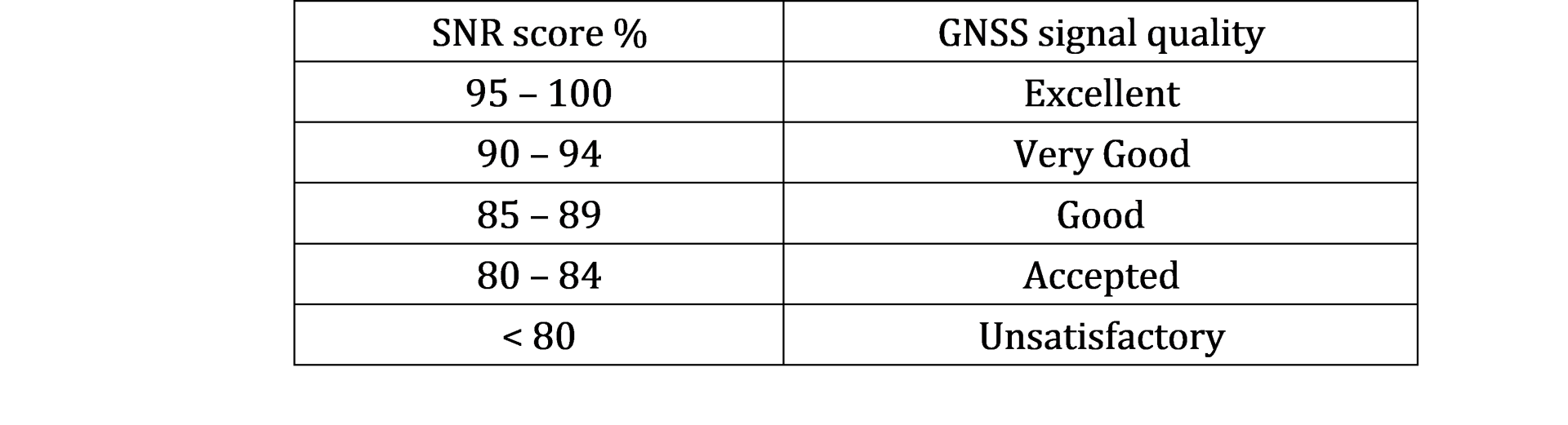
For SinoGNSS products, a customized message KSXT is defined to display the SNR score information, which is also designed for dual-antenna GNSS receivers. As shown in the message below, the red parameters indicate the SNR score of the master antenna and slave antenna in turn. And the signal quality for both antenna is excellent.
$KSXT,20210906104914.00,121.29239578,31.34996850,33.3672,276.66,43.34,83.17,0.102,0.00,1,3,39,42,,,,0.101,0.012,0.143,96,95,*21
The abnormal SNR reflects the magnitude of the interference affected by the signal. Usually, the SNR on the 1Hz bandwidth is used as the signal quality indicator. The magnitude of the SNR will directly affect the performance of signal capture and tracking, and also affect the performance of the entire positioning solution. It is an index to measure the reliability of acquisition and tracking, and can be used to screen satellites suitable for participating in the navigation and positioning solution.
For more GNSS messages information, please refer to the OEM command manual of ComNav Technology or directly contact our support team via support@comnavtech.com
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNav Technology
ComNav Technology develops and manufactures GNSS OEM boards and receivers for high precision positioning demanded applications. Its technology already been used in a wide range of applications such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, unmanned system. With a team dedicated for the GNSS technology, ComNav Technology is trying its best to supply reliable and competitive products to worldwide customers. ComNav Technology has been listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange (Science and Technology Board), securities :ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 688592.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
About ComNavTech®
ComNavTech® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in People's Republic of China, EU, USA and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.





